| . |  |
. |
| . |  |
. |
|
by Staff Writers San Antonio TX (SPX) Mar 30, 2021
The SwRI-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) orbiting Jupiter aboard NASA's Juno spacecraft has detected new faint aurora features, characterized by ring-like emissions, which expand rapidly over time. SwRI scientists determined that charged particles coming from the edge of Jupiter's massive magnetosphere triggered these auroral emissions. "We think these newly discovered faint ultraviolet features originate millions of miles away from Jupiter, near the Jovian magnetosphere's boundary with the solar wind," said Dr. Vincent Hue, lead author of a paper accepted by the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics. "The solar wind is a supersonic stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun. When they reach Jupiter, they interact with its magnetosphere in a way that is still not well understood." Both Jupiter and Earth have magnetic fields that provide protection from the solar wind. The stronger the magnetic field, the larger the magnetosphere. Jupiter's magnetic field is 20,000 times stronger than Earth's and creates a magnetosphere so large it begins to deflect the solar wind 2-4 million miles before it reaches Jupiter. "Despite decades of observations from Earth combined with numerous in-situ spacecraft measurements, scientists still do not fully understand the role the solar wind plays in moderating Jupiter's auroral emissions," said SwRI's Dr. Thomas Greathouse, a co-author on this study. "Jupiter's magnetospheric dynamics, the motion of charged particles within its magnetosphere, is largely controlled by Jupiter's 10-hour rotation, the fastest in the solar system. The solar wind's role is still debated." One of the goals of the Juno mission, recently approved by NASA for an extension until 2025, is to explore Jupiter's magnetosphere by measuring its auroras with the UVS instrument. Previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope and Juno have allowed scientists to determine that most of Jupiter's powerful auroras are generated by internal processes, that is the motion of charged particles within the magnetosphere. However, on numerous occasions, UVS has detected a faint type of aurora, characterized by rings of emissions expanding rapidly with time. "The high-latitude location of the rings indicates that the particles causing the emissions are coming from the distant Jovian magnetosphere, near its boundary with the solar wind," said Bertrand Bonfond, a co-author on this study from Belgium's Liege University. In this region, plasma from the solar wind often interacts with the Jovian plasma in a way that is thought to form "Kelvin-Helmholtz" instabilities. These phenomena occur when there are shear velocities, such as at the interface between two fluids moving at different speeds. Another potential candidate to produce the rings are dayside magnetic reconnection events, where oppositely directed Jovian and interplanetary magnetic fields converge, rearrange and reconnect. Both of these processes are thought to generate particle beams that could travel along the Jovian magnetic field lines, to eventually precipitate and trigger the ring auroras on Jupiter. "Although this study does not conclude what processes produce these features, the Juno extended mission will allow us to capture and study more of these faint transient events," Hue said.
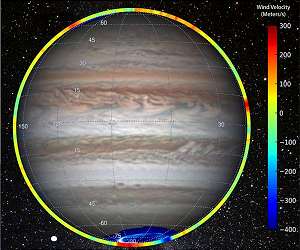
SwRI scientists help identify the first stratospheric winds measured on Jupiter San Antonio TX (SPX) Mar 19, 2021 Working with a team led by French astronomers, Southwest Research Institute scientists helped identify incredibly powerful winds in Jupiter's middle atmosphere for the first time. The team measured molecules exhumed by the 1994 impact of comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 to trace winds in excess of 900 miles per hour near Jupiter's poles. Jupiter's distinctive red and white bands of swirling clouds allow scientists to track winds in the planet's lower atmosphere, and the SwRI team members have particular exp ... read more
|
|||||||||||||
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2026 - SpaceDaily. All websites are published in Australia and are solely subject to Australian law and governed by Fair Use principals for news reporting and research purposes. By using our websites you consent to cookie based advertising. If you do not agree with this then you must stop using the websites from May 25, 2018. Privacy Statement. Additional information can be found here at About Us. |