| . |  |
. |
Paris, France (ESA) Oct 22, 2004 A team of European astronomers has discovered that many stars in the vicinity of the Sun have unusual motions caused by the spiral arms of our galaxy, the Milky Way. According to this research, based on data from ESA's Hipparcos observatory, our stellar neighbourhood is the crossroads of streams of stars coming from several directions. Some of the stars hosting planetary systems could be immigrants from more central regions of the Milky Way. The Sun and most stars near it follow an orderly, almost circular orbit around the centre of our galaxy, the Milky Way. Using data from ESA's Hipparcos satellite, a team of European astronomers has now discovered several groups of 'rebel' stars that move in peculiar directions, mostly towards the galactic centre or away from it, running like the spokes of a wheel. These rebels account for about 20% of the stars within 1000 light-years of the Sun, itself located about 25 000 light-years away from the centre of the Milky Way. The data show that rebels in the same group have little to do with each other. They have different ages so, according to scientists, they cannot have formed at the same time nor in the same place. Instead, they must have been forced together. "They resemble casual travel companions more than family members," said Dr Benoit Famaey, Universite Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium. Famaey and his colleagues believe that the cause forcing the rebel stars together on their unusual trajectory is a 'kick' received from one of the Milky Way's spiral arms. The spiral arms are not solid structures but rather regions of higher density of gas and stars, called 'density waves' and similar to traffic hot-spots along the motorway. An approaching density wave compresses the gas it encounters and favours the birth of new stars, but it can also affect pre-existing stars by deflecting their motion. After the wave has passed, many stars will thus travel together in a stream, all in the same direction, even though they were originally on different trajectories or not even born. This research has shown that the neighbourhood of the Sun is a crossroads of many streams, made up of stars with different origins and chemical composition. These streams could also account for many of the stars with planetary systems recently discovered near the Sun. Astronomers know that stars with planetary systems preferentially form in dense gas clouds with a high metal content, such as those located in the more central regions of the Milky Way. The streams discovered by Hipparcos could be the mechanism that brought them closer to the Sun. As Famaey explains, "If these stars are kicked by a spiral arm, they can be displaced thousands of light-years away from their birthplace." These stars, together with their planets, can thus have migrated closer to the Sun. To learn more about the structure of our Milky Way, an aggregate of thousands of millions of stars, astronomers look at the way in which stars stay together in a coherent way or move with respect to the Sun and relative to one another. During its four-year mission, ESA's Hipparcos satellite has measured the distance and motion of more than a hundred thousand stars within a 1000 light-years of the Sun. However, while Hipparcos's data show in which directions stars are moving on the sky, they cannot tell whether stars are coming towards us or going away from us. By combining the Hipparcos data with ground-based measurements of their 'Doppler shift', obtained with a Swiss telescope at the Observatoire de Haute-Provence, France, Famaey and his colleagues could add the missing third dimension, namely the speed with which stars approach us or recede from us. Because of the Doppler shift, the colour of a star appears to change when it travels towards us or away from us, becoming respectively bluer or redder and giving astronomers information about its motion. "By combining all these first-class data, we now have a comprehensive, three-dimensional view of how nearby stars move about us," said Famaey. Scientists now wonder how widespread are the streams discovered by Famaey's team and what role they could play in the evolution of our galaxy. "This result opens up exciting new prospects for our understanding of the dynamics of the Milky Way," said Dr Michael Perryman, ESA Hipparcos and Gaia project scientist. ESA's forthcoming mission Gaia, scheduled for launch in 2011, will make it possible to extend this investigation over a much wider region of our galaxy. Gaia will observe more than a thousand million stars and will measure their motion in all three dimensions simultaneously, thanks to the on-board spectrograph providing information on their Doppler shift. "This will give us the clearest view ever of the structure and evolution of the Milky Way," Perryman said.
Related Links
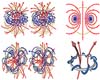 Garching, Germany (SPX) Oct 19, 2004
Garching, Germany (SPX) Oct 19, 2004Just how does one explain the enormous magnetic field strengths of the so-called 'magnetic stars'? This question concerning magnetic fields in the cosmos, first posed half a century ago, has now been answered by scientists of the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics in Garching. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |