| . |  |
. |
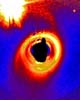
Edinburgh - Dec 01, 2003 Astronomers at the Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Councils UK Astronomy Technology Centre (ATC) at the Royal Observatory, Edinburgh have produced compelling new evidence that Vega, one of the brightest stars in the sky, has a planetary system around it which is more like our own Solar System than any other so far discovered. All of the hundred or so planets that have been discovered around other stars have been very large gaseous (Jupiter-like) planets orbiting close to their star. This is very unlike our own Solar System. New computer modelling techniques have shown that observations of the structure of a faint dust disk around Vega can be best explained by a Neptune-like planet orbiting at a similar distance to Neptune in our own solar system and having similar mass. The wide orbit of the Neptune-like planet means that there is plenty of room inside it for small rocky planets similar to the Earth * the Holy Grail for astronomers wanting to know whether we are alone in the Universe. The modelling, which is described today (1 December 2003) in The Astrophysical Journal, is based on observations taken with the world's most sensitive submillimetre camera, SCUBA. The camera, built at the ATC, is operated on the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope in Hawaii. The SCUBA image shows a disk of very cold dust (-180 degrees centigrade) in orbit around the star. "The irregular shape of the disk is the clue that it is likely to contain planets" explains astronomer Mark Wyatt, the author of the paper. "Although we can't directly observe the planets, they have created clumps in the disk of dust around the star." The modelling suggests that the Neptune-like planet actually formed much closer to the star than its current position. As it moved out to its current wide orbit over about 56 million years, many comets were swept out with it, causing the dust disk to be clumpy. "Exactly the same process is thought to have happened in our Solar System", said Wyatt, "Neptune was 'pushed' away from the Sun because of the presence of Jupiter orbiting inside it". So it appears that as well as having a Neptune-like planet, Vega may also have a more massive Jupiter-like planet in a smaller orbit. The model can be tested in two ways as Wayne Holland, who made the original observations, explains "The model predicts that the clumps in the disk will rotate around the star once every three hundred years. If we take more observations after a gap of a few years we should see the movement of the clumps. Also the model predicts the finer detail of the disk's clumpiness which can be confirmed using the next generation of telescopes and cameras." Paradoxically the star barely appears in the SCUBA image because it is far too hot to be seen with this kind of detector. Vega is, however, easily seen with the naked eye. It is the third brightest star visible from Northern latitudes and is bluish-white in colour. Tonight you can see it in the west at around 7 pm. Related Links The Royal Observatory, Edinburgh Joint Astronomy Center PPARC SpaceDaily Search SpaceDaily Subscribe To SpaceDaily Express
 Pasadena - Oct 21, 2003
Pasadena - Oct 21, 2003Just as anthropologists sought "the missing link" between apes and humans, astronomers are embarking on a quest for a missing link in planetary evolution. Only instead of dusty fields and worn shovels, their laboratory is the universe, and their tool of choice is NASA's new Space Infrared Telescope Facility. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2006 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA PortalReports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additionalcopyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |